pySHRED and NuSHRED
Shallow Recurrent Decoders (SHRED) are a novel class of neural networks designed for efficient and accurate state estimation from few sparse sensor measurements.
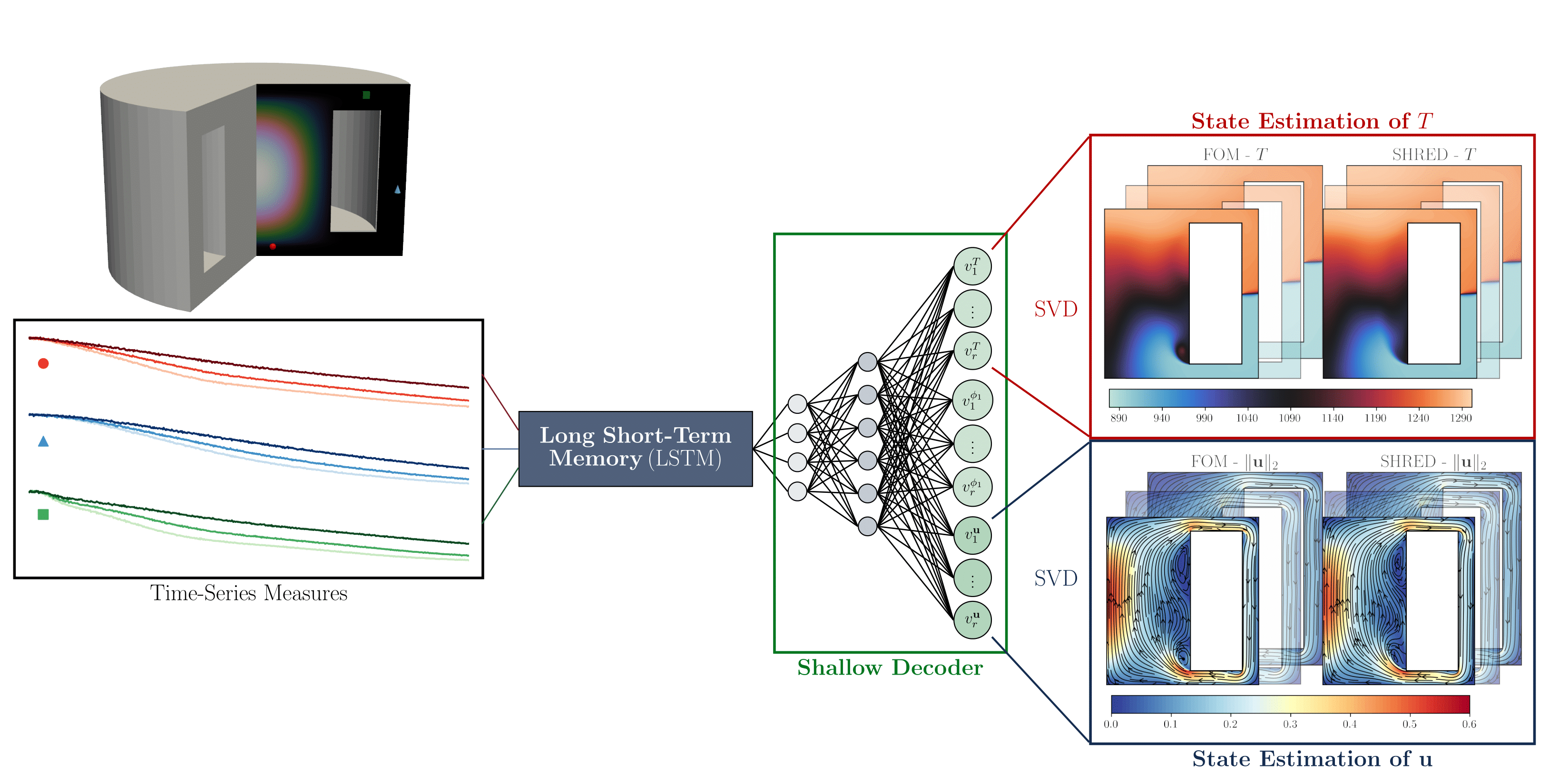
The original SHRED has been proposed by Jan P. Williams et al. (2022) for spatial-temporal data reconstruction.
